News

Feb 12, 2025
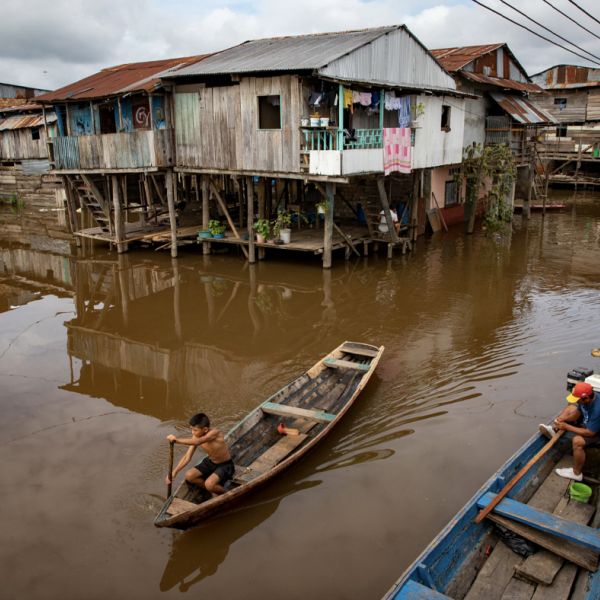
Stuckeman School exhibition to showcase urban floodplain communities in Peru
The international traveling exhibition will run from Feb. 17 to March 4 in the Borland Project Space at 125 Borland Building Penn State University Park.
Full Article

Feb 11, 2025
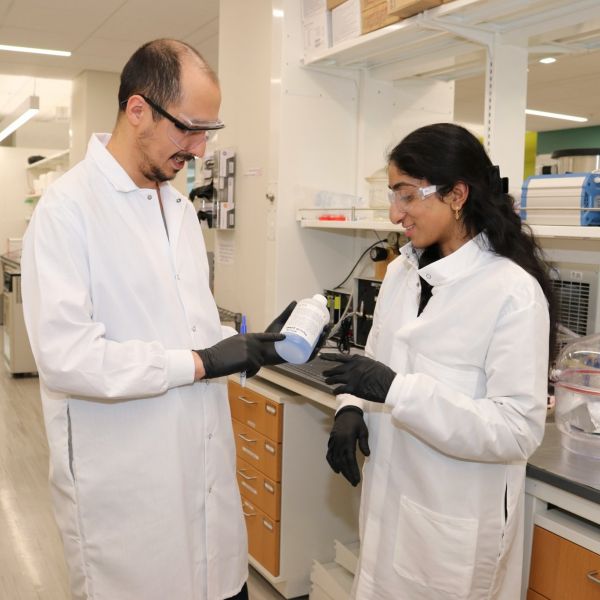
Sustainable Labs Program increases participant engagement, welcomes new labs
Two upcoming virtual sessions will cover how labs can learn more and join next year’s cohort.
Full Article
Feb 06, 2025
Understanding aging requires more than counting birthdays
Types of tissue samples matter when measuring a person’s biological age, or how well their body is functioning, researchers report.
Full Article
Feb 04, 2025
Novel ‘living’ biomaterial aims to advance regenerative medicine
A biomaterial that can mimic certain behaviors within biological tissues could advance regenerative medicine, disease modeling, soft robotics and more, according to researchers at Penn State.
Full Article

Jan 28, 2025
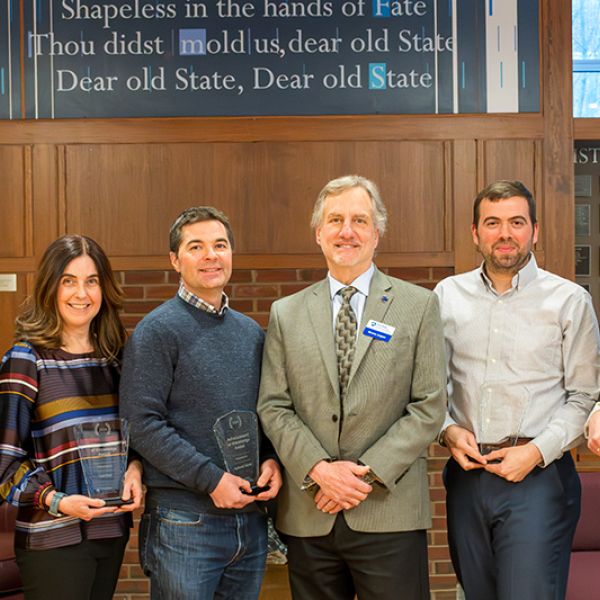
Researchers recognized for excellence by Institute of Energy and the Environment
The Institute of Energy and the Environment recognized six Penn State faculty members for their research excellence.
Full Article

Jan 27, 2025
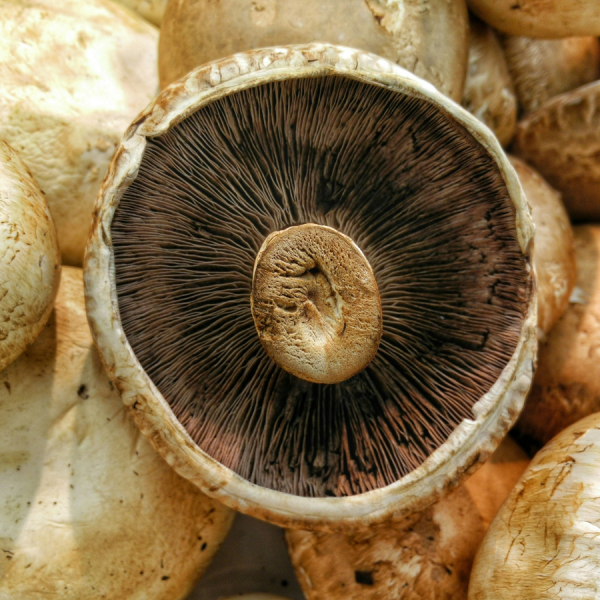
Harnessing mushroom microbiomes for better crop development
Microorganisms collected from the material in which button mushrooms are grown may benefit the development of future fungi crops, according to a study led by researchers in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences and published in the journal Fungal Biology.
Full Article

Jan 23, 2025
$17.9M NIH grant to research neurodevelopment disorders
Illuminating key biological pathways that underlie neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders, such as autism spectrum disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, is the goal of a new five-year, $17.9 million grant from the National Institutes of Health’s National Institute of Mental Health to a national team of researchers.
Full Article

Jan 21, 2025
Christina Grozinger to lead Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences as director
Christina Grozinger, Publius Vergilius Maro Professor of Entomology and director of the Center for Pollinator Research, has been named the new director of the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State.
Full Article

Jan 17, 2025
Discovery could eliminate need to refrigerate vaccines and protein-based drugs
A new storage technique can keep protein-based drugs and vaccines stable without keeping them cold. The discovery, led by researchers at Penn State, could eliminate the need for refrigeration for hundreds of life-saving medicines like insulin, monoclonal antibodies and viral vaccines.
Full Article

Jan 07, 2025
Quantity over quality? Different bees are attracted to different floral traits
When it comes to deciding where they’re going to get their next meal, different species of bees may be attracted to different flower traits, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State and published in PNAS Nexus.
Full Article