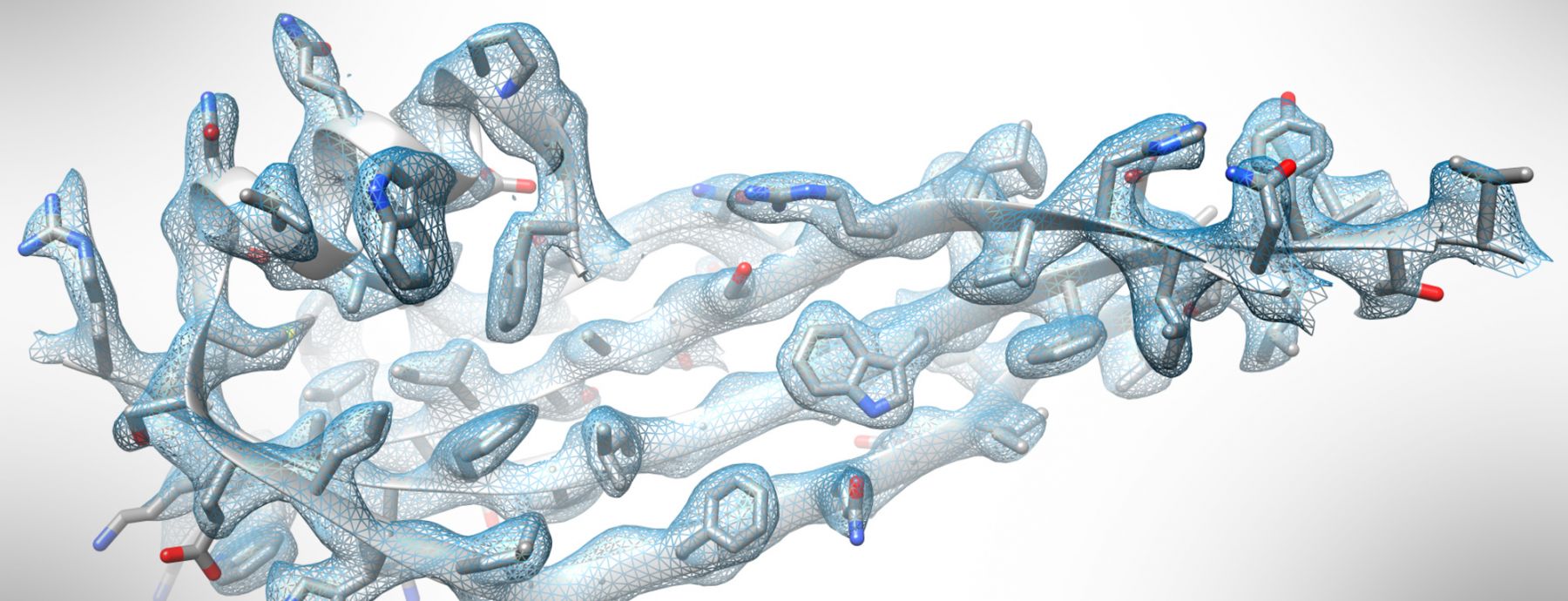
Structural biology provides a detailed three-dimensional view of molecules that guides the determination of mechanisms driving many cellular processes. The primary goal of the Center is to make transformative advances in the field of structural biology available across Penn State to complement the on-going research of our productive scientists.
Novel developments in the field of cryogenic electron-microscopy (cryo EM) have opened possibilities for studying dynamic behavior of macromolecules at atomic resolutions. The University has augmented the disciplines of crystallography and NMR with the acquisition of state-of-the-art electron microscopes and recruitment of additional expert researchers skilled in high-resolution cryo-EM.
In addition, the center links biomedical engineering, computational resources, material scientists, and machine learning experts to find novel approaches and solutions. Thus the center is an interdisciplinary resource that links scientists across multiple departments, colleges, and campuses.