News

Dec 02, 2019
Bushmeat may breed deadly bacteria
People who eat wildebeests, warthogs and other wild African animals may be at risk for contracting potentially life-threatening diseases, according to an international team of researchers. The team analyzed samples of bushmeat — meat derived from wildlife — in the Western Serengeti in Tanzania and identified several groups of bacteria.
Full Article

Nov 26, 2019
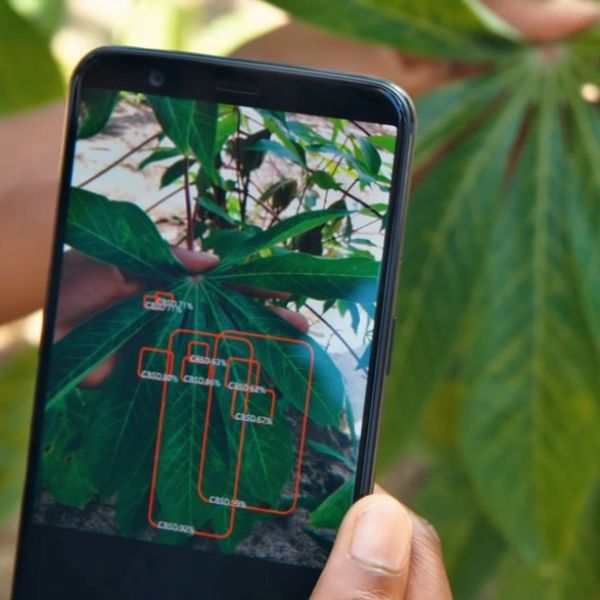
Grant will support expanded use of artificial intelligence for crop health
A research team developing artificial-intelligence-based solutions for diagnosing and managing threats to crop health has received a grant to expand the technology to assist more smallholder farmers around the world.
Full Article

Oct 31, 2019
Malaria parasite lives on the edge
The parasite that causes malaria expresses genes that code for the proteins it will need in later life stages, using two separate schemes to prevent these proteins from actually being made until they are needed, according to new research.
Full Article

Sep 24, 2019
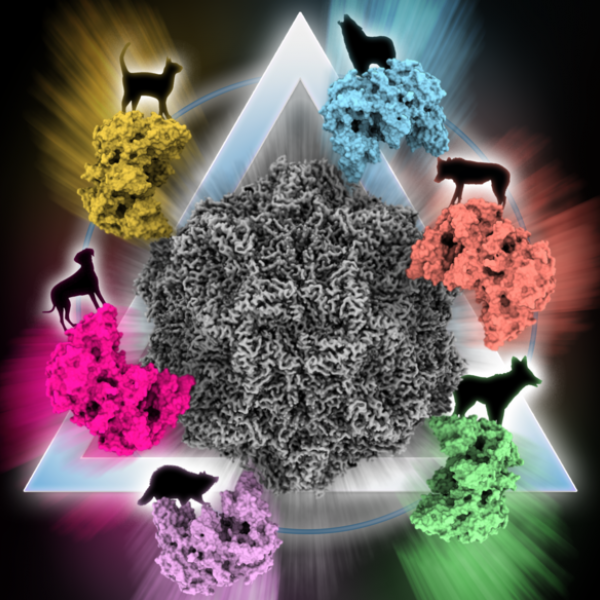
Virus may jump species through 'rock-and-roll' motion with receptors
Like a janitor thumbing through a keychain to find just the right key to open a lock, the "rock-and-roll" motion of the canine parvovirus during the binding process may help explain how the virus can find the spot on a receptor to infect not just dogs, but multiple species, according to an international team of researchers.
Full Article
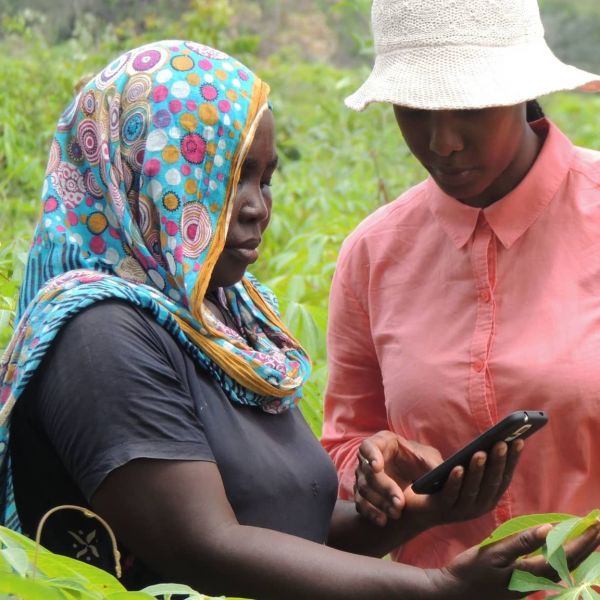

Sep 24, 2019
New AI app predicts climate change stress for farmers in Africa
A new artificial intelligence (AI) tool available for free in a smartphone app can predict near-term crop productivity for farmers in Africa and may help them protect their staple crops — such as maize, cassava and beans — in the face of climate warming, according to Penn State researchers.
Full Article
Sep 19, 2019
New tool in fight against malaria
Redesigning molecules originally developed to treat the skin disease psoriasis could lead to an effective new drug against malaria, according to an international team of researchers.
Full Article
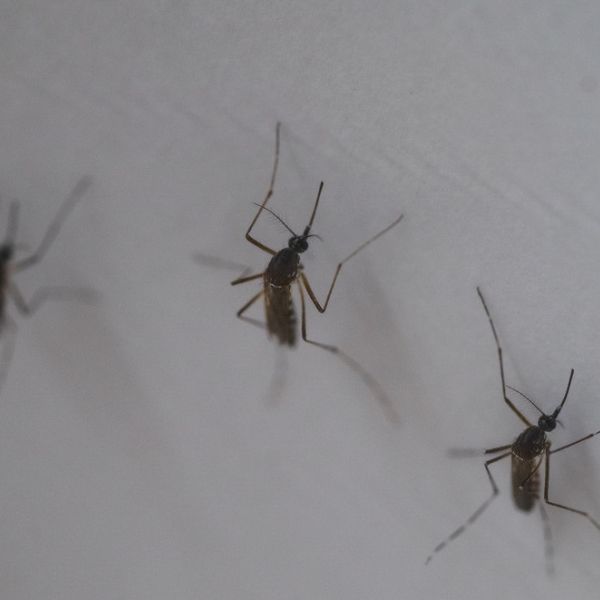

Aug 27, 2019
Research predicts stability of mosquito-borne disease prevention
More than half of the people in the world, including in the United States, live alongside Aedes aegypti — the mosquito that transmits dengue, Zika and other often deadly viruses. Dengue virus, alone, infects nearly 400 million people worldwide each year.
Full Article

Jul 17, 2019
New tuberculosis tests pave way for cow vaccination programs
Skin tests that can distinguish between cattle that are infected with tuberculosis (TB) and those that have been vaccinated against the disease have been created by an international team of scientists.
Full Article

Jul 09, 2019
PlantVillage gives undergraduate a chance to help feed the world via technology
Coming from the small town of Limeport, near Allentown, a young Annalyse Kehs may not have thought much about international agriculture or feeding the world. But thanks to a project called PlantVillage, the Penn State rising senior not only is helping to address world hunger but is relishing the opportunity to travel to destinations such as Kenya and Rome to interact with farmers, researchers and policymakers.
Full Article

Jul 02, 2019
Forecasting infectious diseases: Improved prediction could transform treatment
By applying the same predictive strategies used in weather forecasting, Penn State’s Steven Schiff is changing the way we approach treatment of infectious diseases worldwide.
Full Article