News
Feb 07, 2025
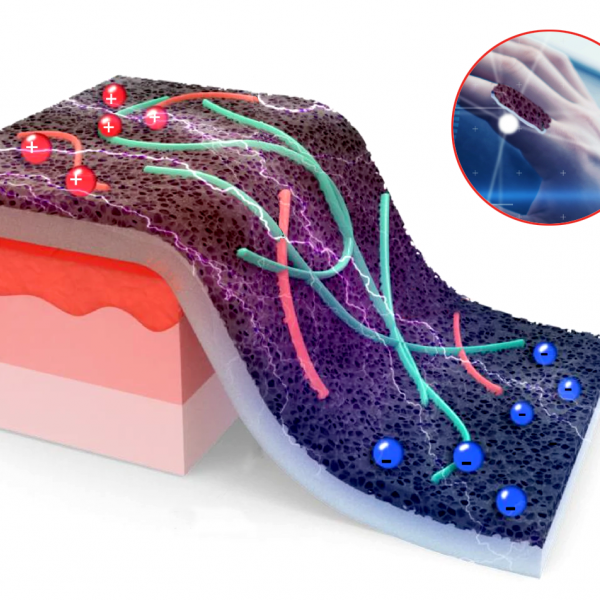
New smart sensor takes the pain out of wound monitoring
Laser-made, ultra-thin material enables precise, self-powered tracking of healing wounds.
Full Article

Jan 21, 2025
Christina Grozinger to lead Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences as director
Christina Grozinger, Publius Vergilius Maro Professor of Entomology and director of the Center for Pollinator Research, has been named the new director of the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State.
Full Article

Jan 07, 2025
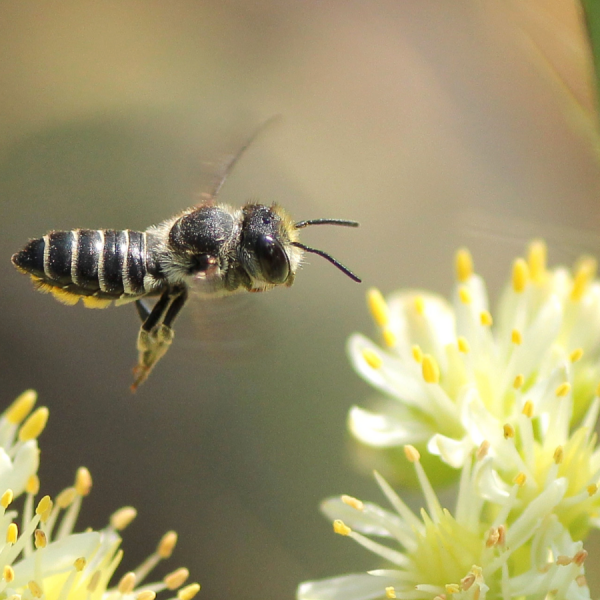
Quantity over quality? Different bees are attracted to different floral traits
When it comes to deciding where they’re going to get their next meal, different species of bees may be attracted to different flower traits, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State and published in PNAS Nexus.
Full Article
Dec 17, 2024
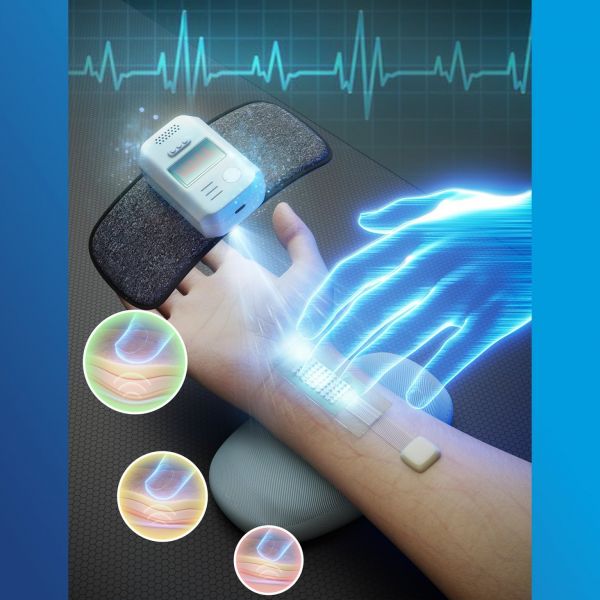
Old wisdom meets new tech: Traditional Chinese medicine inspires pulse sensors
A team led by Penn State researchers used principles of pulse monitoring in traditional Chinese medicine to design a pressure-sensing platform to identify the optimal pulse signal, which they combined with a machine learning model to also predict blood pressure.
Full Article

Oct 14, 2024
Penn State researchers earn funding for sustainable weed and insect management
Three Penn State research teams have received awards totaling $1.78 million from the U.S. Department of Agriculture's National Institute of Food and Agriculture to investigate climate-smart approaches to pest control in agriculture.
Full Article

Oct 02, 2024
Plant compound used in traditional medicine may help fight tuberculosis
A compound found in African wormwood — a plant used medicinally for thousands of years to treat many types of illness — could be effective against tuberculosis.
Full Article

Sep 26, 2024
Plant scientist named Huck Early Career Chair in Microbial Community Ecology
Francisco Dini-Andreote, assistant professor of plant science in the College of Agricultural Sciences at Penn State, has been awarded the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Early Career Chair in Microbial Community Ecology.
Full Article

Jul 19, 2024
Penn State professor named to advisory board of National Smell and Taste Center
Penn State sensory expert John Hayes has been appointed to the external scientific advisory board of the newly established National Smell and Taste Center at the National Institutes of Health (NIH).
Full Article
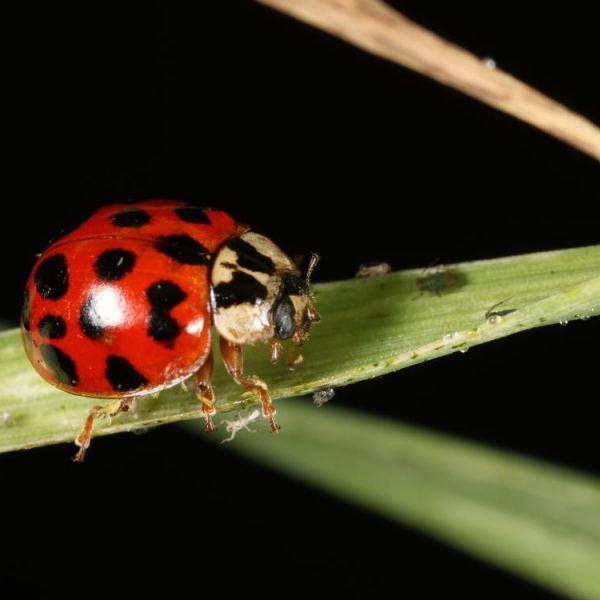

Feb 22, 2024
Ladybug scents offer a more ecologically friendly way to protect crops
The use of pesticides, while beneficial for global food security, wreaks havoc on natural ecosystems and human health. To address this issue, Penn State researchers have turned to an unlikely enforcer to protect crops: the ladybug.
Full Article

Nov 28, 2023
Researchers predict climate change-driven reduction in beneficial plant microbes
Bacteria that benefit plants are thought to be a critical contributor to crops and other ecosystems, but climate change may reduce their numbers, according to a new study by an international team of researchers. They published their findings in Nature Food.
Full Article