News

Jul 02, 2025
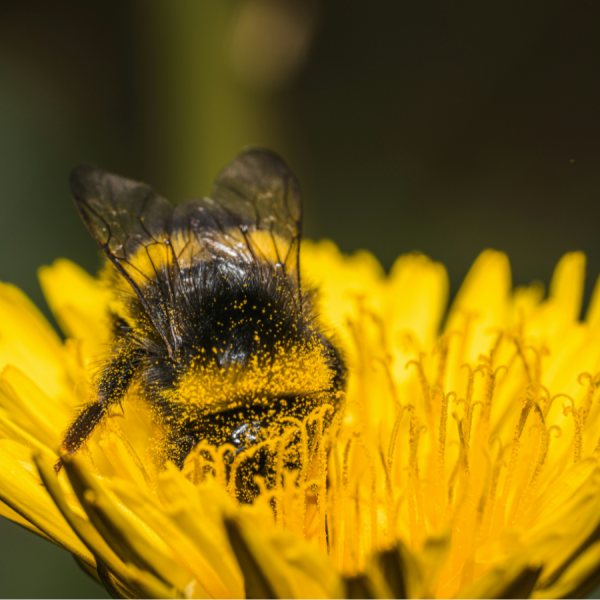
What a bumble bee chooses to eat may not match ideal diet
A new study led by researchers at Penn State suggests that what bumble bees choose to eat may not line up with their ideal nutritional needs.
Full Article

Jun 25, 2025
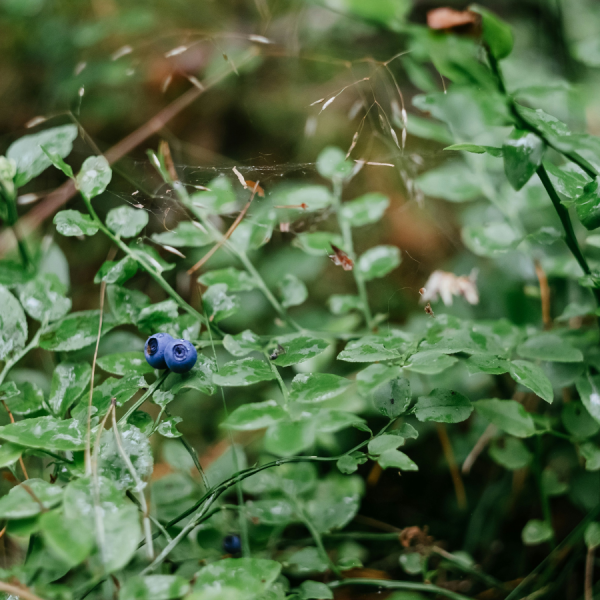
Warmer spots within fields have more blooms and more bees
Climate can vary across large areas of land, but it also can vary within much smaller areas such as farms. A new study by researchers at Penn State examined whether these microclimates — the climate of a very small or restricted area — affect pollination by both wild and managed bees and resulting wild blueberry yields.
Full Article

Jun 20, 2025
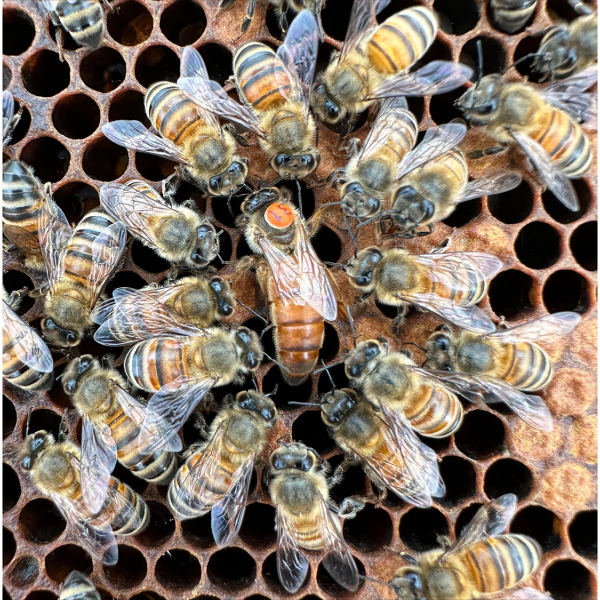
How a genetic tug-of-war decides the fate of a honey bee
Despite having identical genetic instructions, female honey bee larvae can develop into either long-lived reproductive queens or short-lived sterile workers who help rear their sisters rather than laying their own eggs. Now, an interdisciplinary team led by researchers at Penn State has uncovered the molecular mechanisms that control how the conflict between genes inherited from the father and the mother determine the larva’s fate.
Full Article

Jun 11, 2025
‘Fingerprinting’ plant compounds helps explain food, drink tastes
Researchers develop method to determine what compounds affect bitter taste, mouthfeel in wine, dark chocolate, and other foods and drinks.
Full Article
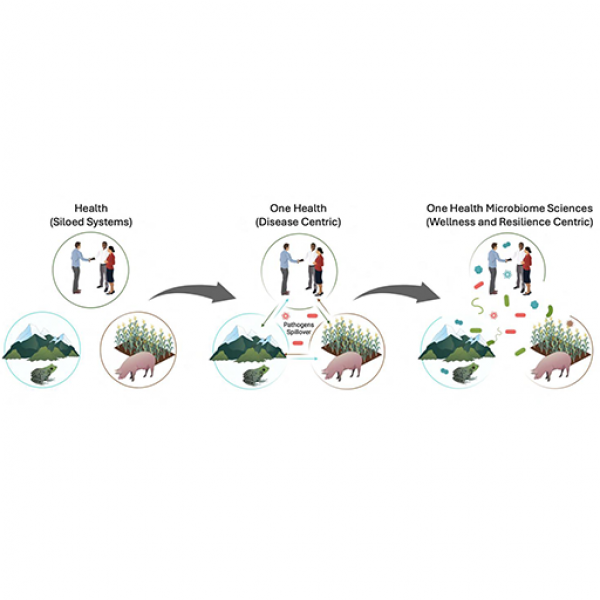
Jun 11, 2025
Q&A: Unifying the microbiome sciences for global health and sustainability
Recently, members of Penn State's One Health Microbiome Center published an article in the American Society for Microbiology’s flagship journal, mBio. In this Q&A, a few of the paper’s authors discussed how the center is leading the charge to breakdown traditional disciplinary silos and expand the One Health focus to include more than just pathogenic microbial threats.
Full Article

May 29, 2025
Biology professor, Huck associate operations director to retire
After a decade of service to the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and a distinguished academic career spanning four decades, James Marden, professor of biology and associate director of operations, will retire from Penn State at the end of June.
Full Article
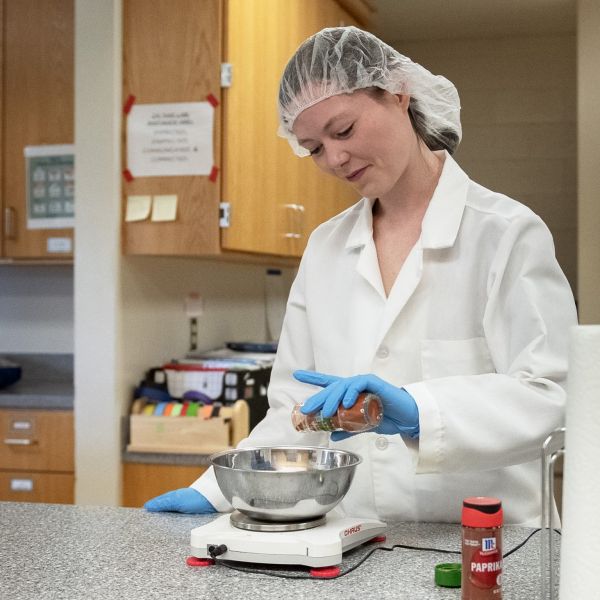

May 22, 2025
Looking to cut calories? Try adding chilies, study suggests
Throwing a little heat on your meal might be an effective strategy for cutting back on calories, according to a new study led by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article
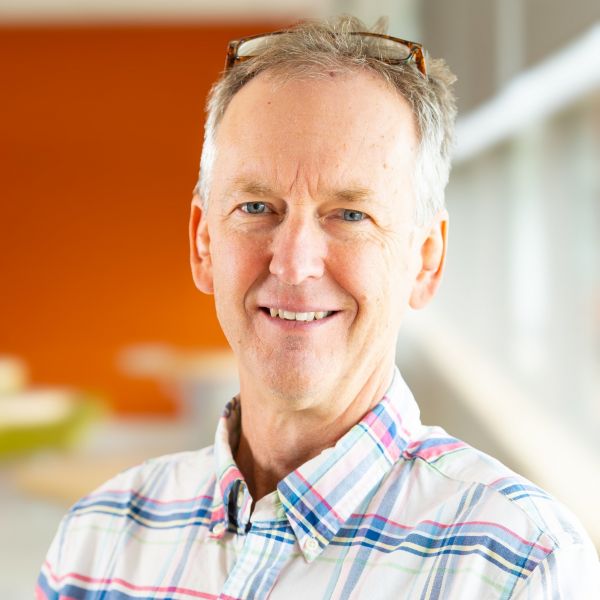

Apr 30, 2025
Celebrating James Marden: A Decade of Impact and a Lifetime of Achievement
After a decade of exceptional service to the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and a distinguished academic career spanning four decades, James Marden, professor of biology and associate director of operations, will retire from Penn State at the end of June 2025.
Full Article
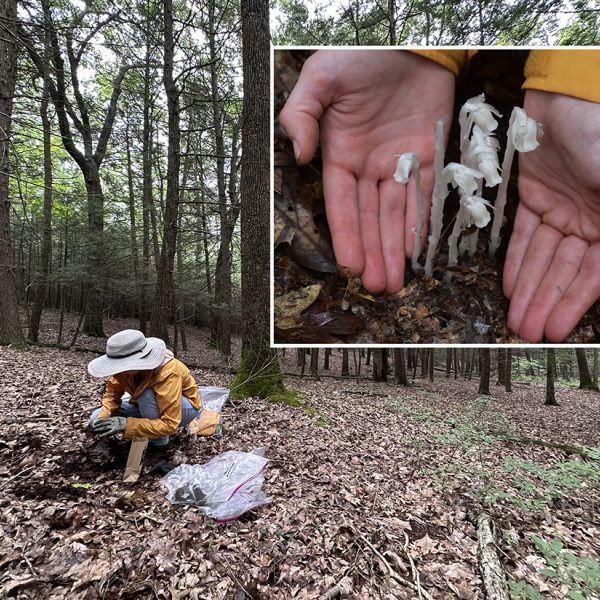

Apr 25, 2025
Traditional forest medicinal plant ghost pipe used differently today
Driven by the internet and social media, consumption of a strange white plant known as ghost pipe is enjoying a resurgence — but with a twist.
Full Article
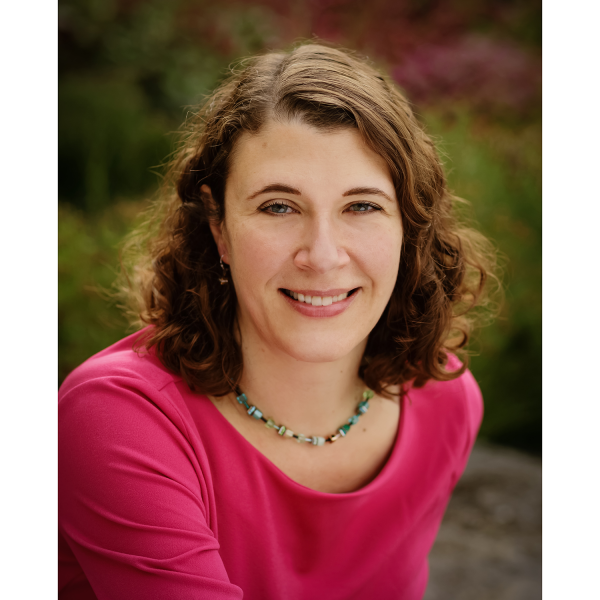

Apr 24, 2025
Grozinger appointed to National Academies committee on insect declines
The National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine recently appointed Christina Grozinger, Publius Vergilius Maro Professor of Entomology and director of the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences at Penn State, to an 18-member study committee to examine the status of insects in North America.
Full Article