News

Jan 21, 2025
Feb. 5 lecture to discuss how sleep health affects daily life, long-term health
Orfeu Buxton, Elizabeth Susman Professor of Biobehavioral Health, will present the 2025 Pattishall Research Lecture
Full Article

Jan 17, 2025
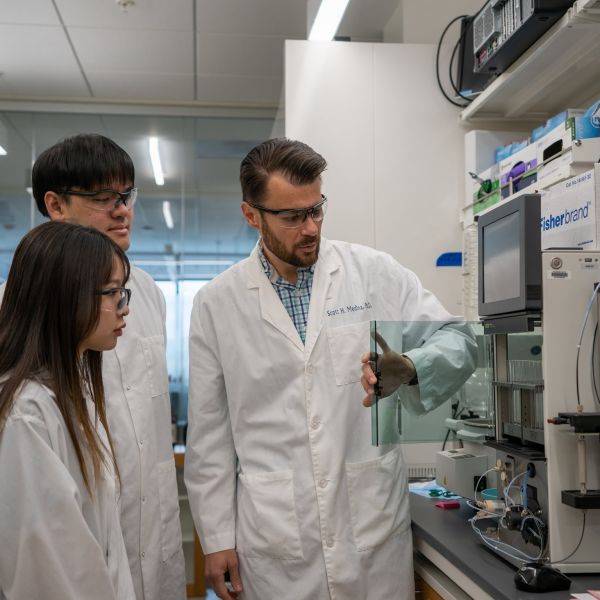
Discovery could eliminate need to refrigerate vaccines and protein-based drugs
A new storage technique can keep protein-based drugs and vaccines stable without keeping them cold. The discovery, led by researchers at Penn State, could eliminate the need for refrigeration for hundreds of life-saving medicines like insulin, monoclonal antibodies and viral vaccines.
Full Article

Jan 06, 2025
Fourth annual Big Ten Neuroscience Symposium to convene at Penn State
The Penn State Neuroscience Institute, through the Huck Institutes of the Life Sciences and the Penn State College of Medicine, will host the Big Ten Neuroscience Annual Meeting on July 21 and 22 at the Nittany Lion Inn in State College.
Full Article

Jan 28, 2025
New Annual Summit Focuses on Graduate Student Resiliency
Earlier this month, the Huck Institutes, in partnership with the J. Jeffrey and Ann Marie Fox Graduate School at Penn State, hosted the Inaugural Huck Institutes T32 Summit.
Full Article
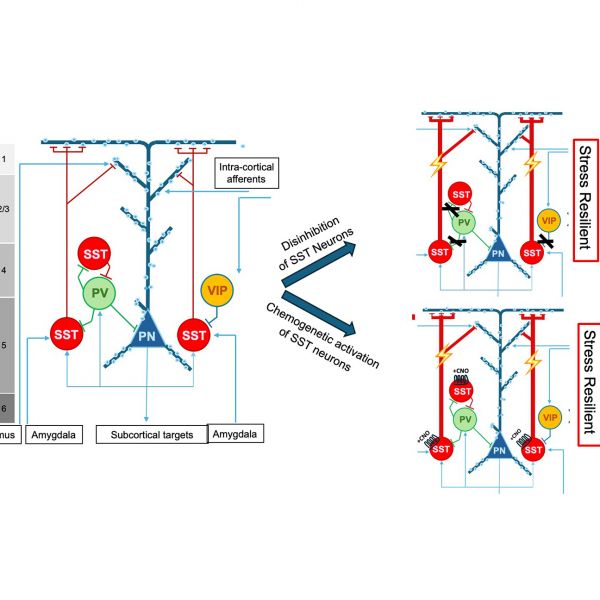
Dec 17, 2024
Brain regions that relieve effects of chronic stress in mice differ based on sex
In two new studies, researchers made mice resilient to stress by activating neurons in different brain regions and found that the changes involved are highly sex-specific
Full Article

Dec 16, 2024
Two Huck graduate students receive American Heart Association fellowships
Two Huck graduate students awarded individual 2-year American Heart Association fellowships.
Full Article
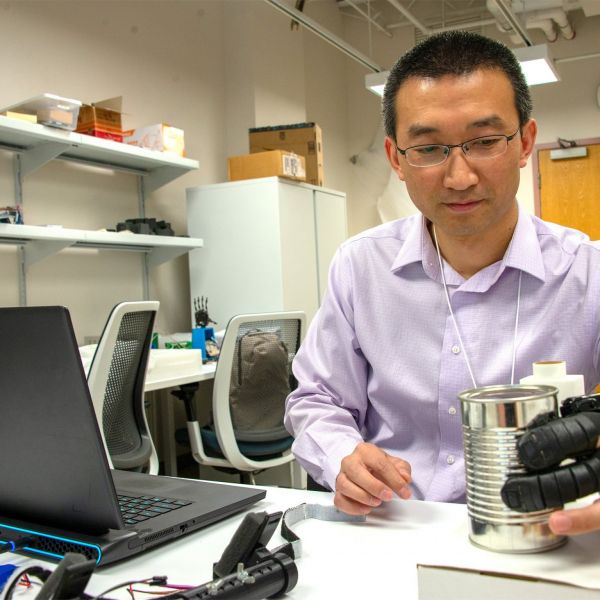

Dec 17, 2024
Person-centered, bio-inspired research leads to improved control of prosthetics
Penn State researcher focuses on creating wearable assistive robotic systems for people with limited use of their limbs, especially their hands, with the goal of the user intuitively controlling the systems and devices on which they rely.
Full Article

Dec 12, 2024
Center for Socially Responsible AI awards seed funding to seven diverse projects
The Penn State Center for Socially Responsible Artificial Intelligence (CSRAI) has announced the results of its most recent seed-funding competition.
Full Article

Dec 12, 2024
Relieving chronic stress in the brains of male and female mice
In two new studies, researchers made mice resilient to stress by activating neurons in different brain regions and show that the brain regions and gene expression changes involved are highly sex-specific.
Full Article
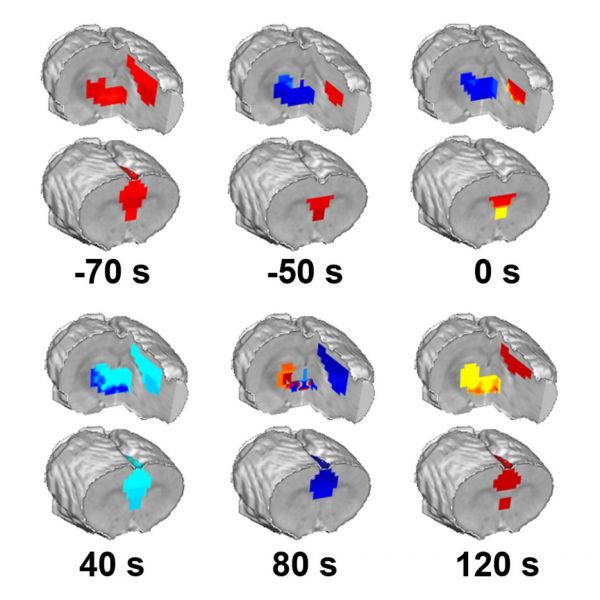
Dec 11, 2024
Brain mechanisms underpinning loss of consciousness identified
Rapid activity in three brain regions appears to trigger loss of consciousness, researchers at Penn State find.
Full Article