News

Apr 25, 2019
Food Scientist Kovac Receives Young Investigator Award
Jasna Kovac, assistant professor of food science in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, recently was named recipient of the Institut Merieux Young Investigator Award in Antimicrobial Resistance from the International Association for Food Protection.
Full Article

Apr 25, 2019
Bacteria uses viral weapon against other bacteria
Bacterial cells use both a virus — traditionally thought to be an enemy — and a prehistoric viral protein to kill other bacteria that competes with it for food according to an international team of researchers who believe this has potential implications for future infectious disease treatment.
Full Article

Apr 24, 2019
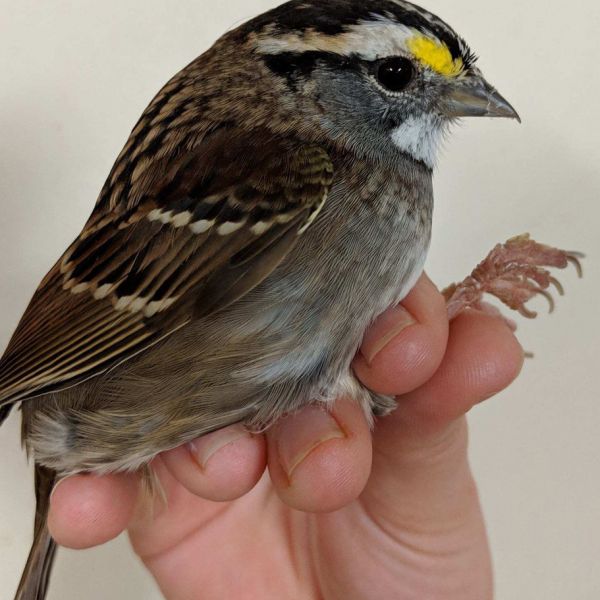
Songbird-body changes that allow migration may have human health implications
Songbirds that pack on as much as 50 percent of their body weight before migrating and that sleep very little, exhibit altered immune system and tissue-repair function during the journey, which may hold implications for human health, according to Penn State researchers.
Full Article

Apr 24, 2019
Ehau-Taumaunu awarded newly established Phytobiomes Fellowship
Hanareia Ehau-Taumaunu, doctoral candidate in the Department of Plant Pathology and Environmental Microbiology in Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, has been selected as the recipient of the Phytobiomes Fellowship for the 2019-20 academic year.
Full Article

Apr 23, 2019
New sensor detects rare metals used in smartphones
A more efficient and cost-effective way to detect lanthanides, the rare earth metals used in smartphones and other technologies, could be possible with a new protein-based sensor that changes its fluorescence when it binds to these metals. A team of researchers from Penn State developed the sensor from a protein they recently described and subsequently used it to explore the biology of bacteria that use lanthanides. A study describing the sensor appears online in the Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Full Article

Apr 19, 2019
NIH Trainees Juan Cerda and Catherine Douds Receive NSF-GRFP Honorable Mentions
Juan Cerda and Catherine Douds, both members of NIH-sponsored training programs overseen by the Huck Institutes, were recognized for their promising research ideas.
Full Article

Apr 17, 2019
Bootcamp for Science Entrepreneurs To Run May 13-17
"The Business of Science" is a week-long opportunity for grad students and postdocs considering nontraditional careers. Applicants must register by April 29, 2019.
Full Article
Apr 17, 2019
Feiyue Lu Wins Simpson Award for Innovative Research
MCIBS student Feiyue Lu's research into RNA in Drosophila flies was recognized for its complexity, scope, and difficulty.
Full Article

Apr 15, 2019
Five Huck Researchers Among Winners at Grad Student Awards
A quintet of Huck doctoral candidates were recognized for excellence in their studies and collaborations within and outside of Penn State.
Full Article

Apr 11, 2019
New SCATTIRSTORM microscope could improve bioenergy production
The construction of a new multimodal optical microscope, SCATTIRSTORM, that could enable more efficient bioenergy production, is the focus of a three-year, $1.5 million, U.S. Department of Energy grant awarded to three Penn State researchers.
Full Article