News

Apr 10, 2025
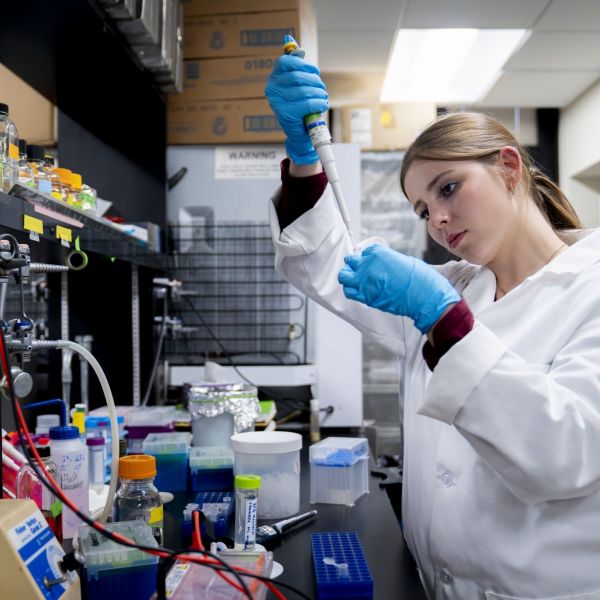
Graduating senior reflects on undergraduate research experiences at Penn State
Maria Lovallo is a Penn State undergrad from Spring Mills, PA, majoring in Microbiology with a minor in Plant Pathology & Environmental Microbiology. She is also a teaching assistant in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, and a member of the Huck Institutes’ One Health Microbiome Center.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
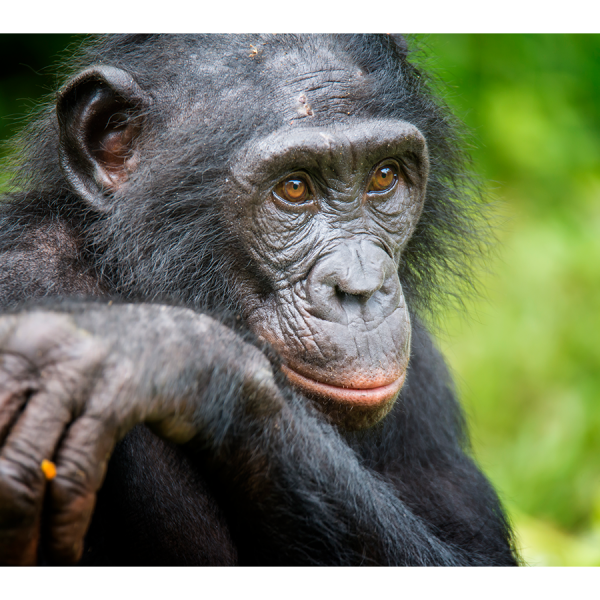
Complete genome sequences of six ape species unveiled
Differences among the DNA of seven ape species — including humans — are greater than originally thought, according to an international team led by researchers at Penn State, the National Human Genome Research Institute, and the University of Washington.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
Postdoctoral training series assists scholars seeking fellowships
Three free sessions cover funding mechanisms, strategies for crafting effective proposals, and feedback to strengthen current fellowship applications.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
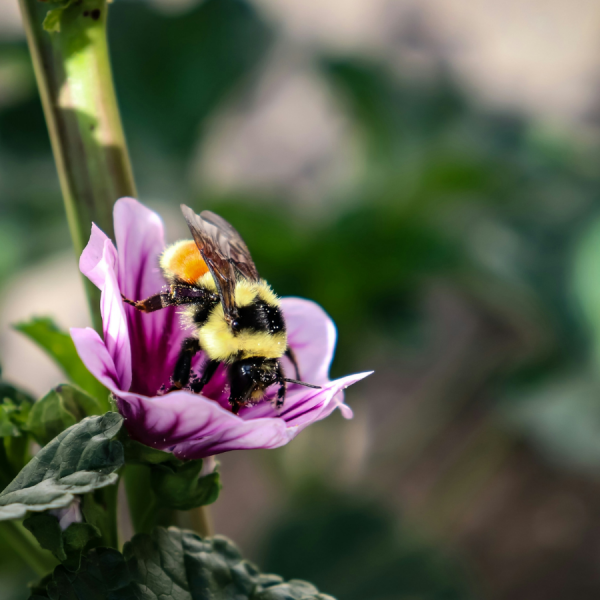
Even sublethal insecticide dose may disrupt pollinator mating process
Insecticides can help protect crops against troublesome pests, but they also pose a risk for beneficial insects such as pollinators. A new study led by researchers at Penn State provided insight into how even sublethal doses of insecticides can negatively affect pollinators by disrupting the mating process.
Full Article
Apr 09, 2025
NCEMS working groups to answer molecular and cellular bioscience questions
The U.S. National Science Foundation National Synthesis Center for Emergence in the Molecular and Cellular Sciences at Penn State aims to drive multidisciplinary collaboration utilizing publicly available research data.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
‘Patchy’ thermogels show next-gen biomedical material potential, scientists say
Special biomedical materials that can be injected as a liquid and turn into a solid inside our bodies — called thermogels — could provide a less-invasive way to deliver drugs or treat wounds. Scientists at Penn State have developed a new design for these materials that further improves their properties and may hold particular promise for use in tissue regeneration, the researchers said.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
Complete genome sequences of six ape species unveiled
Previously inaccessible regions reveal novel insights that may advance understanding of evolution and conservation genetics for endangered apes as well as human health.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
Penn State Schuylkill biologist recognized as a PERC Campus Sustainability Champion
The Pennsylvania Environmental Resource Consortium (PERC) has named Mary Ann Smith, lecturer of biology at Penn State Schuylkill, as a 2025 Campus Sustainability Champion.
Full Article

Apr 09, 2025
Q&A: Can artificial intelligence growth and sustainability go hand in hand?
Optimizing AI to use less energy and protect the environment
Full Article

Apr 08, 2025
Feeding dairy cows whole cottonseed byproduct boosts milk fat, researchers find
In a new study, a team led by researchers at Penn State demonstrated that supplementing dairy cattle feed with 15% whole cottonseed can increase milk fat concentration and yield.
Full Article