News

Jul 16, 2025
When dreams turn dark: Neuroscientists to study nightmares and mental health
Dreams, and likely nightmares, are experienced universally across humans and animals, but neuroscientists still do not know why. Now, with a three-year, $1.2 million grant from the W.M. Keck Foundation, an interdisciplinary team of researchers at Penn State will study the underlying mechanisms of nightmares and their relationship with anxiety-related mental health disorders, such as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD).
Full Article
Jul 16, 2025
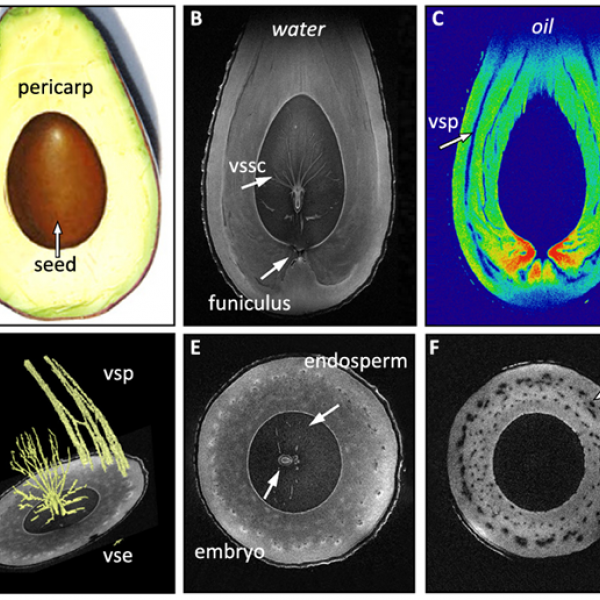
MRI advancements herald new possibilities for plant imaging
Magnetic resonance imaging is an established tool for human medical diagnostics, but recent advancements mean that it now offers plant researchers unprecedented capabilities for non-invasive visualization of plant structures and systems.
Full Article

Jul 15, 2025
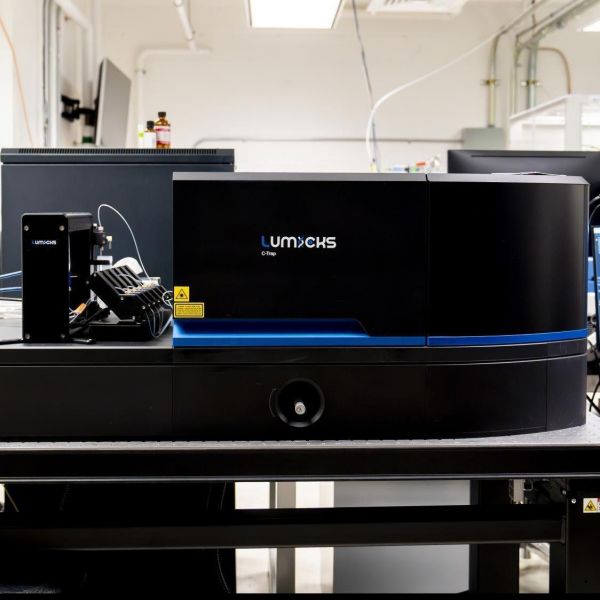
Optical tweezers help elevate single-molecule research at Penn State
The instrument, supported by a new NIH infrastructure grant, uses laser light to ‘tweeze’ tiny objects like DNA molecules and proteins.
Full Article

Jul 15, 2025
Grant to help establish AI, health research lab at Harrisburg
A pair of Penn State Harrisburg faculty have been awarded funding to establish a research lab focused on using artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) to improve health care access and outcomes.
Full Article

Jul 15, 2025
What if Pennsylvania apples disappeared?
Penn State’s fruit tree task force helps farmers protect both their harvest and their future. From hands-on support to innovative blossom-thinning techniques, the work of Penn State researchers and educators is vital for the success of agriculture across the commonwealth.
Full Article

Jul 14, 2025
The breadth of the brain
Researchers in the Penn State Neuroscience Institute study the brain’s many aspects in a variety of ways, with implications from mental health to aging and disease.
Full Article
Jul 09, 2025
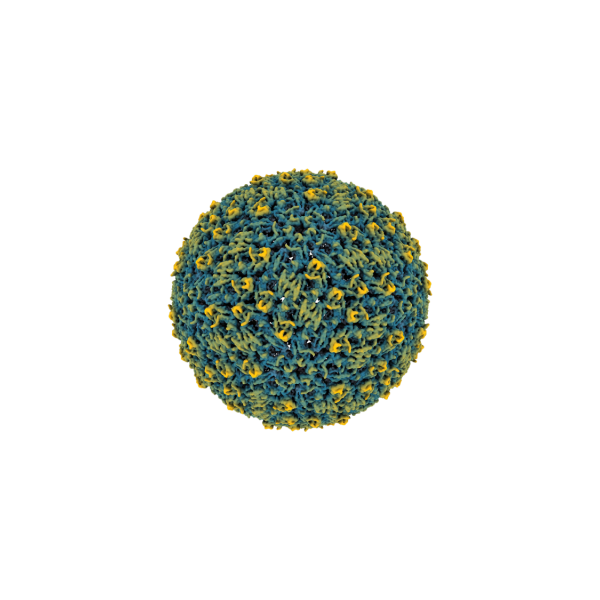
Structure of tick-borne virus revealed at atomic resolution for the first time
Rates of the Powassan virus infections — which can cause seizures and paralysis — are increasing across commonwealth, nation.
Full Article
Jul 09, 2025
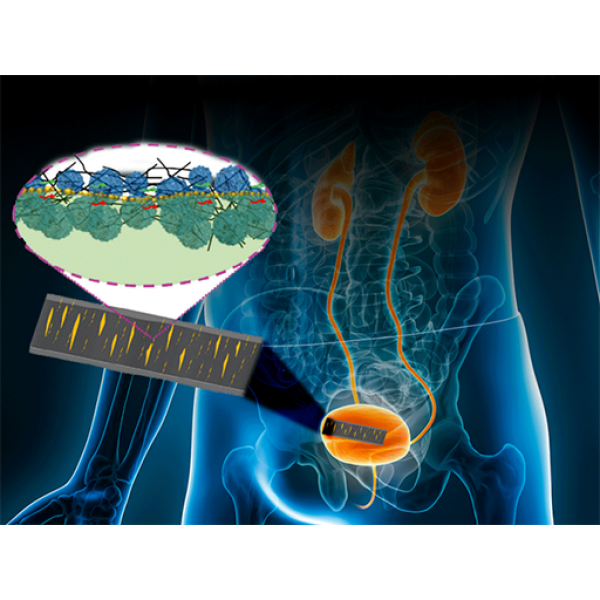
Skin-like sensor monitors internal, external body movement, electrical signals
A new skin-like sensor developed by an international team led by researchers at Penn State could help doctors monitor vital signs more accurately, track healing after surgery and even help patients with bladder control issues.
Full Article

Jul 08, 2025
Fungicides intended to suppress turfgrass diseases may damage fairways
Golf course managers have much more insight into which fungicides to use to suppress turfgrass diseases, such as the common and costly dollar spot disease, without damaging the grass on their fairways, thanks to a new study by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article

Jul 08, 2025
Q&A: Does adolescent alcohol use impact future risk of addiction?
Postdoctoral fellow Laurel Seemiller studies the biology and long-term consequences of adolescent alcohol usage. In this Q&A, Seemiller spoke about her research and her experience at Penn State.
Full Article