News

Apr 01, 2025
Researchers working to address agricultural greenhouse gas emissions
On the latest episode of “Growing Impact,” a team of Penn State researchers discusses how their seed grant project aims to address nitrous oxide emissions from the agricultural sector by developing a system for real-time emissions monitoring and reduction.
Full Article

Mar 31, 2025
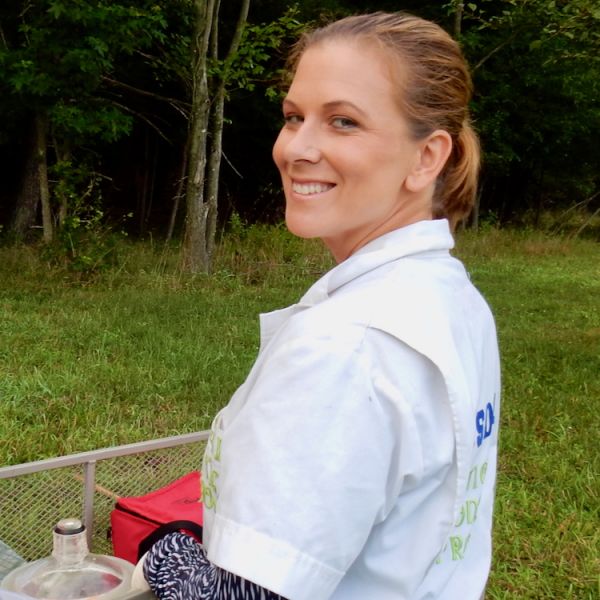
Machtinger harnesses the power of collaboration to solve complex problems
Erika Machtinger is a veterinary entomologist whose work impacts wildlife, agriculture, industry, and public health across the U.S. Her efforts hinge upon the unique, interdisciplinary ecosystem of researchers and resources at Penn State.
Full Article

Mar 24, 2025
Insecticides may contribute to bigger problems with certain weeds
Insecticides may help growers hoping to protect their crops from harmful insects, but they also may contribute to a larger amount of some weeds, according to a study led by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article

Mar 19, 2025
Three deans co-host research scholarship and land grant impacts event March 24
Three Penn State deans are co-hosting an event focusing on role of the University as Pennsylvania’s land-grant institution, the similar role of U.S. land-grant universities and the impacts of scholarly research they produce.
Full Article
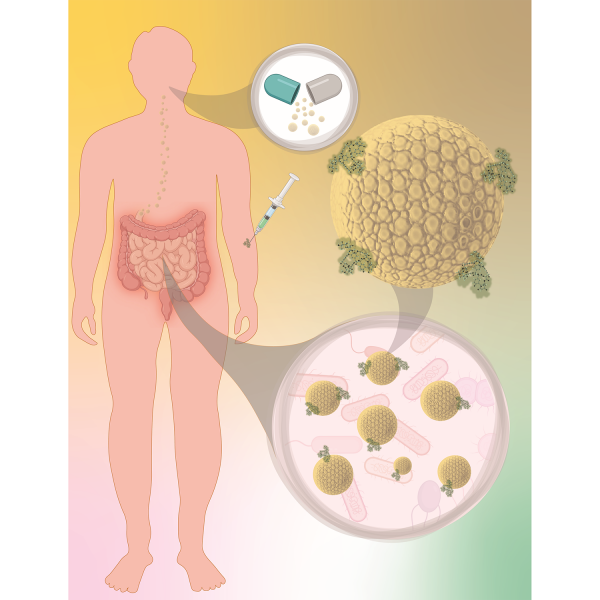
Mar 18, 2025
FDA-approved dialysis drug may help fight against antimicrobial resistance
The study, conducted in mice, revealed that sevelamer can successfully remove off-target antibiotics from the gut.
Full Article
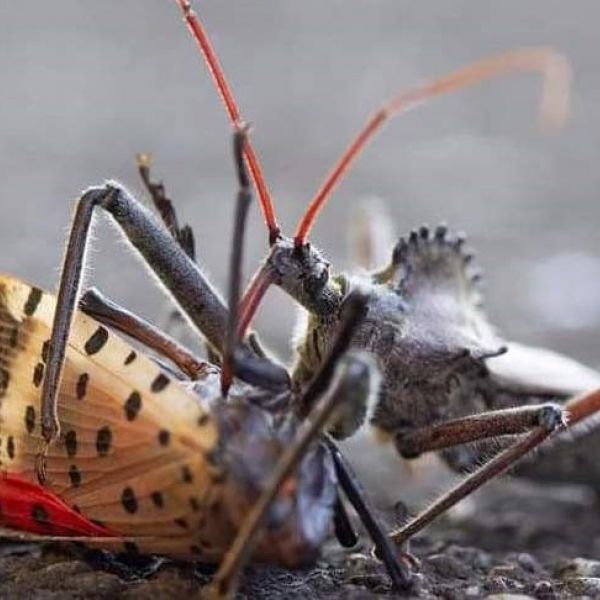

Mar 17, 2025
Natural insect predators may serve as allies in spotted lanternfly battle
Insect predators found in the United States could help keep spotted lanternfly populations in check while potentially reducing reliance on chemical control methods, according to a new study conducted by researchers at Penn State.
Full Article
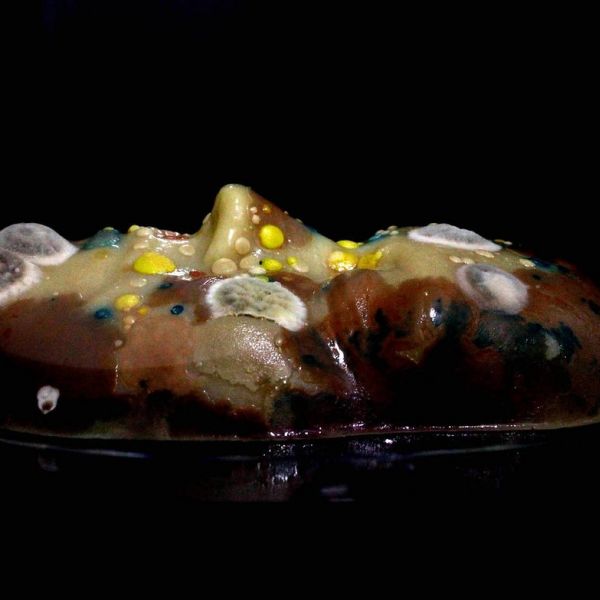

Mar 18, 2025
BioArtist Mellissa Monsoon to present 'Collaborating with Microbes'
The One Health Microbiome Center and College of Arts and Architecture are co-hosting three events as part of a multi-year SciArt collaboration.
Full Article

Mar 17, 2025
Ag Sciences research institute SAFES funds projects addressing critical issues
Penn State’s College of Agricultural Sciences, through its Institute for Sustainable Agricultural, Food and Environmental Science, known as SAFES, announced funding awards to accelerate the advancement of its Critical Issues Initiatives. These initiatives serve as the college’s impact hubs, addressing urgent and high-impact challenges through targeted efforts and innovative projects.
Full Article
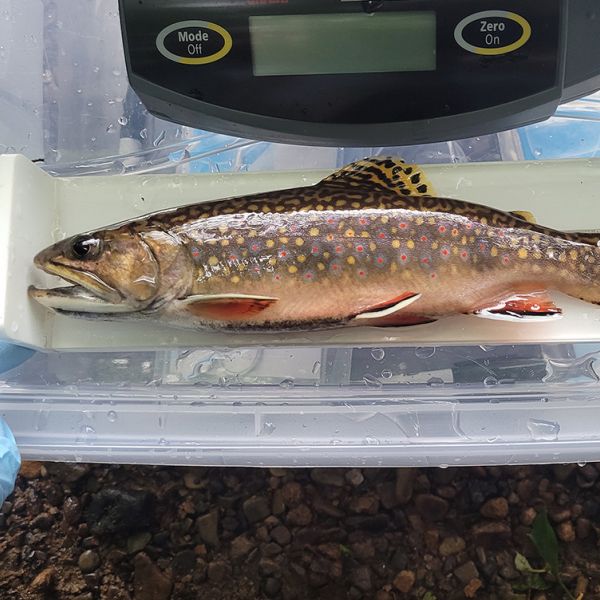

Mar 17, 2025
Threatened by warming waters, brook trout may be able to adapt to hotter weather
Heatwaves appear to trigger heritable gene expression changes that may help make the fish more tolerant of thermal stress, researchers report in novel study.
Full Article
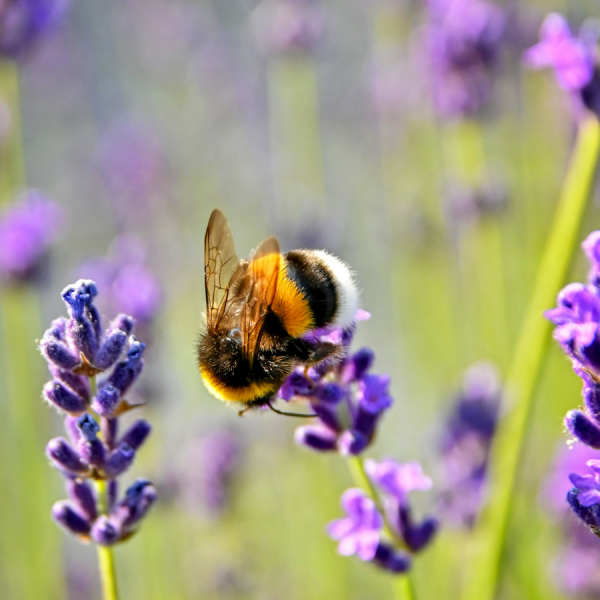

Mar 12, 2025
Analyzing genetic ‘signatures’ may give insight into what stresses wild bees
A new method of examining gene expression patterns called landscape transcriptomics may help pinpoint what causes bumble bees stress and could eventually give insight into why bee populations are declining overall.
Full Article