News

Jun 30, 2025
Huck announces 2025-26 Leadership Fellows
Three faculty members, representing three different Penn State colleges, have been named Huck Leadership Fellows for the 2025-26 academic year.
Full Article

May 08, 2025
Biological physicist Réka Albert elected to National Academy of Sciences
Réka Albert, Evan Pugh University Professor and professor of physics and biology at Penn State, has been elected to the National Academy of Sciences.
Full Article

Apr 21, 2025
Focus on sanitation and clean water may improve control of endemic cholera
Pathogens that persist in hosts and environments may require tailored management strategies, according to new study of endemic cholera interventions in Sub-Saharan Africa.
Full Article
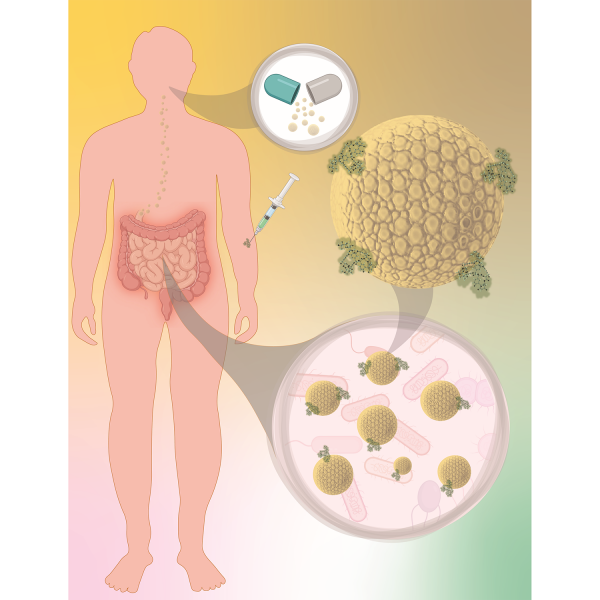
Mar 18, 2025
FDA-approved dialysis drug may help fight against antimicrobial resistance
The study, conducted in mice, revealed that sevelamer can successfully remove off-target antibiotics from the gut.
Full Article

Jul 08, 2024
Re-engineering cancerous tumors to self-destruct and kill drug-resistant cells
A team led by Penn State researchers has created a modular genetic circuit that turns cancer cells into a “Trojan horse,” causing them to self-destruct and kill nearby drug-resistant cancer cells. Tested in human cell lines and in mice as proof of concept, the circuit outsmarted a wide range of resistance.
Full Article
May 30, 2024
Local disparities may prevent national vaccination efforts for rubella
When public health officials make policies about when and how vaccination programs are implemented, they must weigh the benefits and risks of how infectious diseases spread throughout the country. However, these analyses are often based on national-level data and, in some countries, may overlook nuances at the local level.
Full Article

May 06, 2024
Five faculty members honored with Evan Pugh University Professorships
Five Penn State professors—including Huck-affiliated faculty members Reka Albert, Vijaykrishnan Narayanan, and Clive Randall—have been named Evan Pugh University Professors, an elite and prestigious distinction conferred by the University on only 79 faculty members since the establishment of the designation in 1960.
Full Article

May 28, 2024
Réka Albert named Evan Pugh University Professor
Réka Albert, distinguished professor of physics and biology at Penn State, has been named an Evan Pugh University Professor, the highest honor that Penn State bestows on a faculty member.
Full Article

Feb 15, 2024
Lab Bench to Commercialization 2024 grant recipients announced
Four projects led by researchers in the Penn State Eberly College of Science have been selected to receive Lab Bench to Commercialization (LB2C) grants in 2024
Full Article

Dec 05, 2023
Bacteria's mucus maneuvers: Study reveals how snot facilitates infection
New study shows thicker mucus supercharges bacteria’s ability to self-organize into swarms to spread infection
Full Article